Explore a detailed Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala, focusing on its geographical features, political divisions, historical landmarks, and cultural richness. Dive into the country’s diverse landscapes and understand its unique geography.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
A Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala is an essential tool for understanding this Central American country’s diverse geography. Nestled between Mexico, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador, Guatemala boasts a rich topography, from volcanic mountains and dense rainforests to vast plains and coastal regions. Its map reveals not only the country’s physical attributes but also its cultural and historical significance. Understanding the map of Guatemala allows visitors and residents alike to navigate the varied landscapes, uncover hidden gems, and better appreciate the cultural heritage that thrives within its borders. Additionally, studying the map provides a roadmap to exploring the vibrant cities, historical landmarks, and natural wonders scattered throughout this diverse nation.
Geographical Features of Guatemala
The map of Guatemala offers a captivating view of its geographical features, showcasing the country’s dramatic variety. Guatemala is primarily characterized by rugged highlands, coastal plains, and lowland rainforests, offering both natural beauty and ecological diversity. The western and central regions are dominated by a series of mountains and volcanoes, some of which remain active. Famous volcanoes such as Volcán de Fuego, Pacaya, and Atitlán are prominent on the map, attracting adventurers and nature enthusiasts. In addition to these towering geological features, the map highlights numerous lakes, rivers, and valleys that shape Guatemala’s hydrology and ecosystem. For instance, Lake Atitlán, known for its breathtaking scenery, is nestled within volcanic craters and marked on the map as one of Guatemala’s most iconic natural sites.
Volcanoes and Mountain Ranges on the Map of Guatemala
Among Guatemala’s most striking features are its volcanoes and mountain ranges, which are clearly visible on any map of Guatemala. The country sits atop a complex tectonic plate boundary, making it home to some of Central America’s most active volcanoes. Volcanoes like Volcán de Fuego (the “Fire Volcano”) and Volcán Pacaya are prominent and situated along the country’s Pacific coast. These volcanoes not only influence the country’s geography but also play a role in its history, as eruptions have shaped both the landscape and the local cultures. The Sierra Madre mountain range, which stretches across the western part of the country, is another geographical feature prominently depicted on the map of Guatemala. These mountains are home to various indigenous communities, and the terrain can be quite challenging, which adds to the allure of exploring Guatemala’s rugged landscapes.
The Richness of Guatemala’s Coastlines
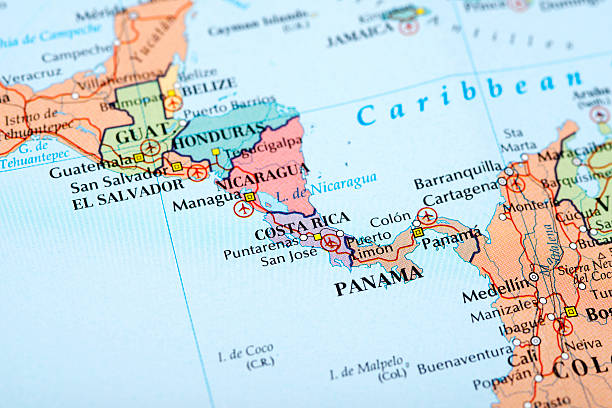
The map of Guatemala also reveals the country’s beautiful coastlines along both the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. On the map, the Pacific coastline is marked by sandy beaches and shallow bays, with Monterrico and Champerico being notable coastal towns. The Caribbean side of Guatemala, although less developed, is equally beautiful, offering lush tropical rainforests and hidden beaches. The Izabal Department, located along the eastern coast, is home to Lake Izabal and the nearby Rio Dulce, both significant bodies of water marked on the map. This diversity in coastal environments highlights Guatemala’s ecological richness, where beaches meet dense jungles, creating unique ecosystems. Exploring Guatemala’s coastal regions provides insight into the biodiversity of the nation, showcasing the contrast between the Pacific and Caribbean coasts.
Key Cities and Regions on the Map of Guatemala
When you study a map of Guatemala, you’ll notice the significant cities and regions that play crucial roles in the country’s cultural, economic, and political spheres. The capital, Guatemala City, is marked prominently on the map. It’s not only the largest city in the country but also a hub of commerce, government, and culture. The map also highlights other important cities such as Quetzaltenango, Guatemala’s second-largest city, known for its colonial architecture and indigenous heritage. Antigua Guatemala, another UNESCO World Heritage site, is located just south of the capital and is marked for its historical significance. Other cities such as Escuintla, Santa Ana, and Chimaltenango are also included on the map, each contributing to Guatemala’s rich cultural fabric. These cities and regions provide a deeper understanding of Guatemala’s urbanization and its historical and cultural legacy.
Exploring Guatemala’s Natural Parks and Reserves
The Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala also underscores the abundance of natural parks and reserves that make the country a haven for ecotourism. With its diverse ecosystems ranging from lush jungles to cloud forests, Guatemala is home to several protected areas. Tikal National Park, marked on the map, is one of the most famous archaeological and ecological sites in Guatemala. The park houses the ruins of the ancient Maya city of Tikal and is a UNESCO World Heritage site. Maya Biosphere Reserve, located in the northeastern region, is another key area on the map, protecting thousands of square kilometers of tropical rainforest. These protected areas, along with other reserves like Lake Atitlán Natural Reserve, show Guatemala’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage for future generations. The country’s network of national parks offers an incredible diversity of flora and fauna, making it a prime destination for wildlife enthusiasts.
The Role of Rivers and Lakes in Guatemala’s Geography
A map of Guatemala also reveals the importance of rivers and lakes in shaping the country’s landscape and providing resources for local populations. The Motagua River, one of Guatemala’s longest rivers, is a central feature on the map. It originates in the highlands and flows eastward to the Caribbean coast, passing through various ecosystems and communities along the way. The Usumacinta River, forming part of the border with Mexico, is another prominent waterway on the map. Guatemala’s lakes, such as Lake Atitlán and Lake Izabal, also stand out on the map due to their ecological and cultural significance. These lakes, often surrounded by volcanic mountains and picturesque towns, are vital to the country’s tourism and local economies. The map illustrates how these bodies of water contribute to the overall environmental balance and livelihood of Guatemala’s people.
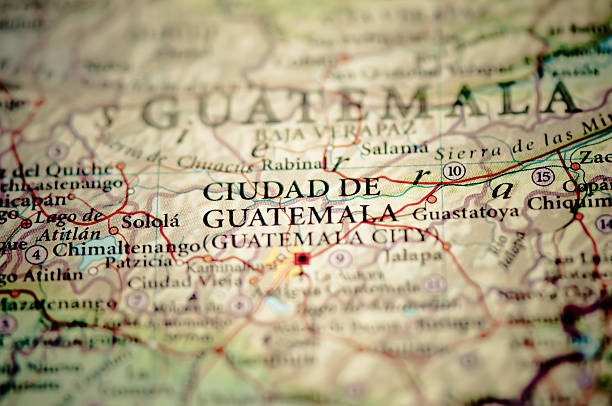
Political Divisions and Departments on the Map of Guatemala
Guatemala’s political structure is highlighted on the map through its 22 departments, each with its own administrative capital. Guatemala City, located in the Guatemala Department, is the country’s center of political power. The map divides the country into distinct regions, each with its own geographical and cultural characteristics. For example, the Petén Department, located in the north, is known for its dense rainforests and ancient Mayan ruins, including Tikal. The Alta Verapaz and Baja Verapaz departments are located in the central highlands, known for their lush vegetation and indigenous communities. Chimaltenango and Sacatepéquez in the south are important for their colonial heritage and proximity to Antigua Guatemala. The map provides insight into the administrative organization of the country, allowing one to explore the diverse cultural and environmental regions that make up Guatemala.
Indigenous Communities and Culture in Guatemala
Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala is home to a rich indigenous heritage, and the map of the country reflects the locations of many Mayan and other indigenous communities. These communities are largely concentrated in the highlands, where languages like K’iche’, Q’eqchi’, and Kaqchikel are still spoken. The Quetzaltenango Department, for example, is a cultural hub for the K’iche’ Maya people, and the map indicates various towns and villages where these languages and traditions are preserved. Chichicastenango, another important site on the map, is famous for its indigenous markets and sacred sites. The map also reflects how these communities have maintained their cultural identity despite the challenges of modernization. Studying the map provides an understanding of the deep connections between Guatemala’s people and their ancestral land.
Historical Landmarks and Sites on the Map of Guatemala
Guatemala is a country steeped in history, and a map of Guatemala highlights numerous historical landmarks that play an integral role in the nation’s past. The ancient city of Tikal, located in the Petén region, is perhaps the most famous historical site in the country, marked clearly on the map as a UNESCO World Heritage site. Other historical landmarks include the colonial city of Antigua Guatemala, marked in the Sacatepéquez Department. The city was once the capital of the Spanish Kingdom of Guatemala and is now a major tourist destination due to its well-preserved architecture and rich history. The map also includes various other Mayan ruins, such as Yaxhá and El Mirador, which are key to understanding the country’s pre-Columbian history. Each of these sites tells a unique story and adds depth to Guatemala’s cultural heritage.
Natural Disasters and Environmental Challenges in Guatemala
Guatemala’s map also reflects the challenges the country faces due to its geological and environmental features. As a country prone to natural disasters like volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and hurricanes, the map highlights areas that are at risk. The Pacaya Volcano is an example of a potentially dangerous natural feature, with the surrounding area marked as one that has experienced eruptions in recent decades. Additionally, the Motagua Fault running through the country is an area susceptible to seismic activity. These geological hazards are an important part of Guatemala’s geography, and understanding them helps in mitigating risks and planning for disaster preparedness. Environmental issues like deforestation and the impact of climate change are also visible on the map through shifts in vegetation and ecosystems, particularly in the Petén region.

Economic Influence of Geography on Guatemala
The economic activities of Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala are closely tied to its geography, and the map of the country can help explain these connections. Regions like the Central Highlands are known for agricultural production, including crops such as coffee, sugar, and vegetables. The Pacific Coast is vital for the fishing and seafood industries, while the Caribbean Coast is known for banana and palm oil cultivation. Guatemala’s proximity to Mexico and the United States also plays a significant role in its economic ties and trade routes. The map illustrates how transportation infrastructure, such as roads and highways, links these different regions to international markets. Understanding the map helps to understand how geography shapes the flow of goods and services within the country.
Conclusion
Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala offers a detailed and multifaceted view of the country, highlighting its rich geography, political structure, historical landmarks, and cultural diversity. By exploring the map, one gains a deeper understanding of Guatemala’s unique landscape and the vibrant people who call it home. From the towering volcanoes and lush rainforests to the colonial cities and ancient Mayan ruins, Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala tells a story of both natural beauty and historical depth. It serves not only as a tool for navigation but also as a gateway to understanding the complexities of a nation rich in culture and history.
Read Also: Enhancing Trading with Trade 12.0 Urex




